
Bills directly influence cash outflows, representing obligations that require cash payment by a specific due date. Effective management of accounts payable helps businesses manage liquidity. Expenses, particularly non-cash items like depreciation, do not involve immediate cash movement but still affect profitability. Accrued expenses, also known as accrued liabilities, net sales are essential for accurately reporting a company’s financial position and performance. On a balance sheet, liabilities show a company’s financial obligations to its lenders and creditors due to past transactions. They occur on the right side of the balance sheet and are divided into current and long-term liabilities.
Accrued Expenses
- When a business uses the Accrual basis accounting method, the revenue is counted as soon as an invoice is entered into the accounting system.
- In addition to the three elements mentioned above, there are two items that are also considered as key elements in accounting.
- For example, the wages your employees earn this month may not be paid until the 1st of the following month.
- The salary expense will reflect the cost of labor to the business, while the salary payable represents both current obligations and future wages.
- Current liabilities are obligations expected to be settled within one year or the operating cycle, whichever is longer.
- Is the transaction a cost you incurred to generate future revenue?
This liability increases at the end of the accounting period and decreases as the money gets paid out. Payroll is one of the most time-consuming accounting tasks—and you need the right tools to work efficiently. Automate the payroll process so you can save time and focus on growing your business.

Ques: What is the Actual difference between prepaid expenses and accrued expenses?

Misclassifications can lead to skewed financial ratios, impacting a company’s perceived profitability, liquidity, and overall financial stability. Capital expenditures (CapEx) are investments in long-term assets like property or equipment, while regular expenses are short-term operational costs. CapEx appears on the balance sheet, while regular expenses affect the income expenses. Recording liabilities involves documenting them as credits in the balance sheet and corresponding debits in an appropriate account (such as cash https://tambopataexpeditions.com/bookkeeping/quickbooks-xero-bookkeeping-cleanup-checklist/ or assets). For example, if you take out a loan, record it as a credit under “Loan Payable” and debit your cash account by the loan amount.
The Importance of Distinguishing Accounts Payable and Accrued Expenses
Non-interest-bearing liabilities, on the other hand, do not involve an explicit interest component, such as accounts payable or accrued expenses. Common examples of expenses include monthly rent for office space or a manufacturing facility. Utility bills for electricity, water, and internet services are recurring costs necessary for business operations. Marketing and advertising costs are also classified as expenses. A liability represents an obligation or debt owed by an individual or business to another entity. These obligations arise from past transactions and require a future outflow of economic benefits, such as cash, goods, or services.
How do I calculate my liability?
- Darcy’s professional experience includes public & governmental accounting as well as small business bookkeeping and tax services.
- These articles and related content is the property of The Sage Group plc or its contractors or its licensors (“Sage”).
- The article “expense vs liability” looks at meaning of and differences between two of these components – expense and liability.
- Capital refers to the net interest in the company and is equal to total assets minus total liabilities.
- One can be easily be confused between prepaid expense vs accrued expense.
- Companies report this amount as payroll expense in their general ledger.
Likewise, increasing assets increases equity, but a decrease in assets lowers equity. Examples of liability accounts that display on the Balance Sheet include Accounts Payable, Sales Tax Payable, Payroll Liabilities, and Notes Payable. Here are a few quick summaries to answer some of the frequently asked questions about liabilities in accounting. Well, the list is quite large and it includes all other charges that help businesses run operations. Diffzy is a one-stop platform for finding differences between similar terms, quantities, services, products, technologies, and objects in one place. Our platform features differences and comparisons, which are well-researched, unbiased, and free to access.
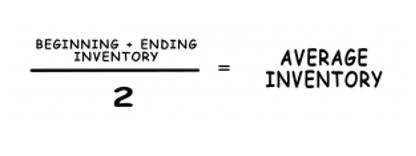
This impact reflects the cost of doing business and consuming resources. Liabilities, while not directly reducing equity in the same way, impact equity indirectly as they represent claims against a company’s assets that must eventually be settled. For instance, receiving upfront payment for a service creates an unearned revenue liability; only when the service is delivered does that liability convert into revenue. Expenses are reported on the income statement, a financial document that summarizes a company’s financial performance over a period, such as a quarter or a year. The income statement subtracts total expenses from total revenues to arrive at net income or loss. This calculation shows how efficiently a business generates profit from its operations.
Companies can record a payroll liability each week by debiting payroll expense and crediting payroll liability. The liability goes away once the company hands difference between expenses and liabilities the accountant a paycheck, resulting in a debit to the payroll liability and a credit to cash. In short, while accounts payable has a short-term cash flow impact, accrued expenses may affect your business more long term, especially if they accumulate over several periods. The placement of expenses and liabilities on financial statements reinforces their distinct nature.


Leave a Reply